Neon Data in Charts [PostgreSQL]
Neon is a modern, scalable cloud platform for PostgreSQL databases designed for developers and teams who need reliable, high-performance data infrastructure.
It also provides AI-powered features in its SQL Editor, allowing you to correct queries, generate sample data, and even create realistic datasets for testing.
In this page, we demonstrate how you can connect PocketQuery to a Neon PostgreSQL database.
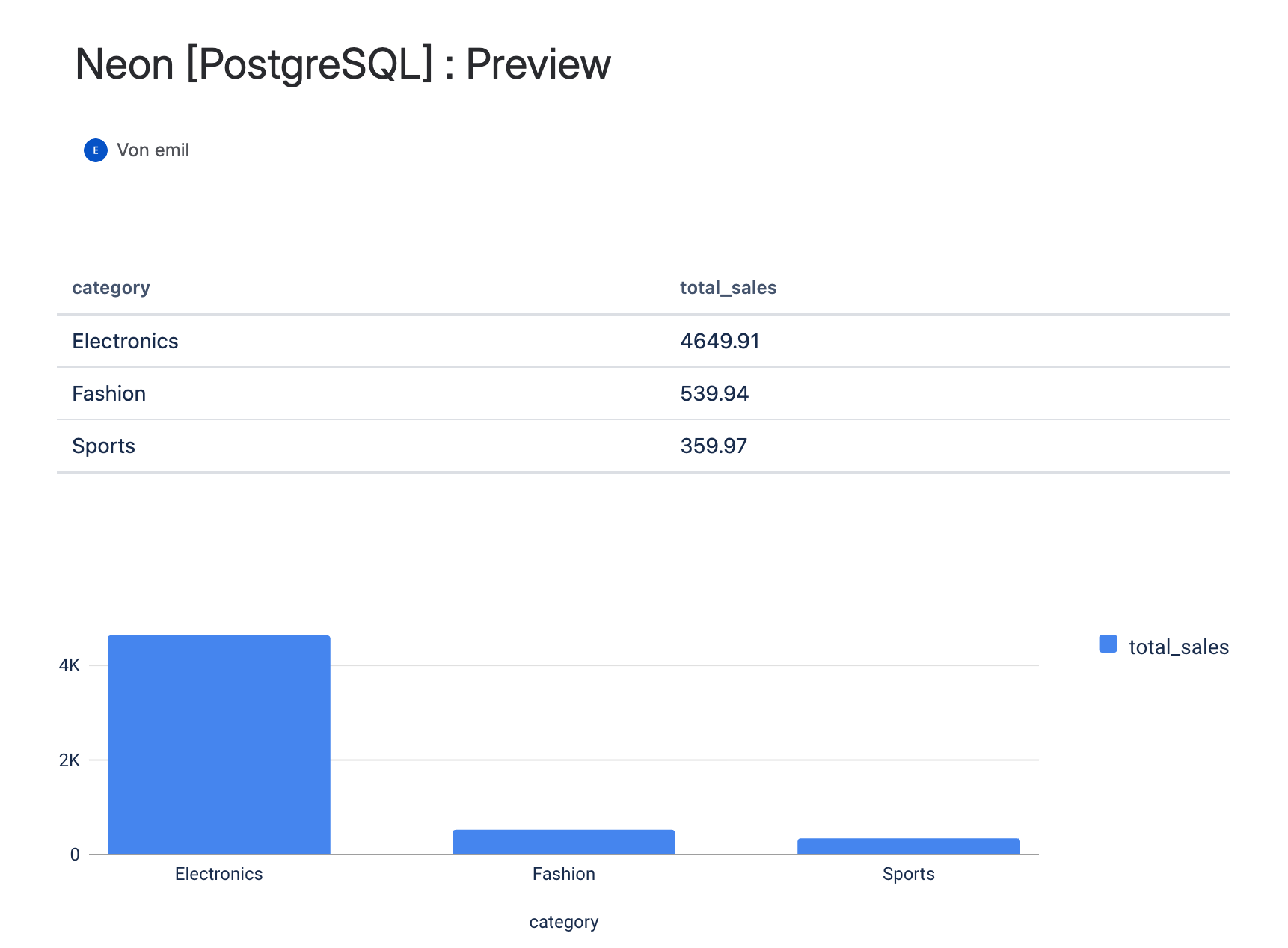
Preview
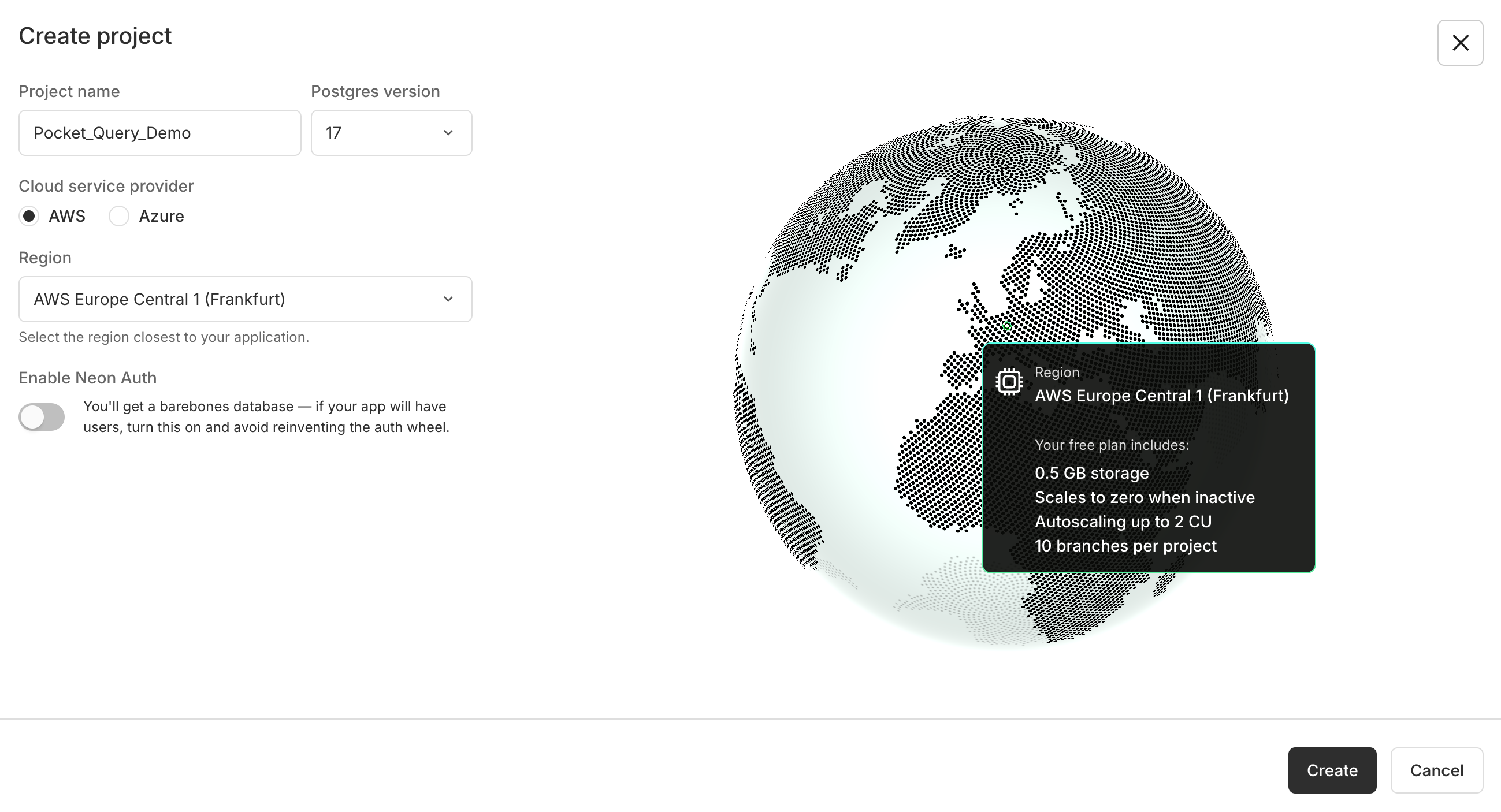
Step 1: Create your first Neon Project
Go to Neon and sign in (you can use GitHub, Google, or email).
Click “Create a new project”.
Enter a Project name and choose the region closest to your location
Neon will automatically create a PostgreSQL database for you, along with a default user and password.
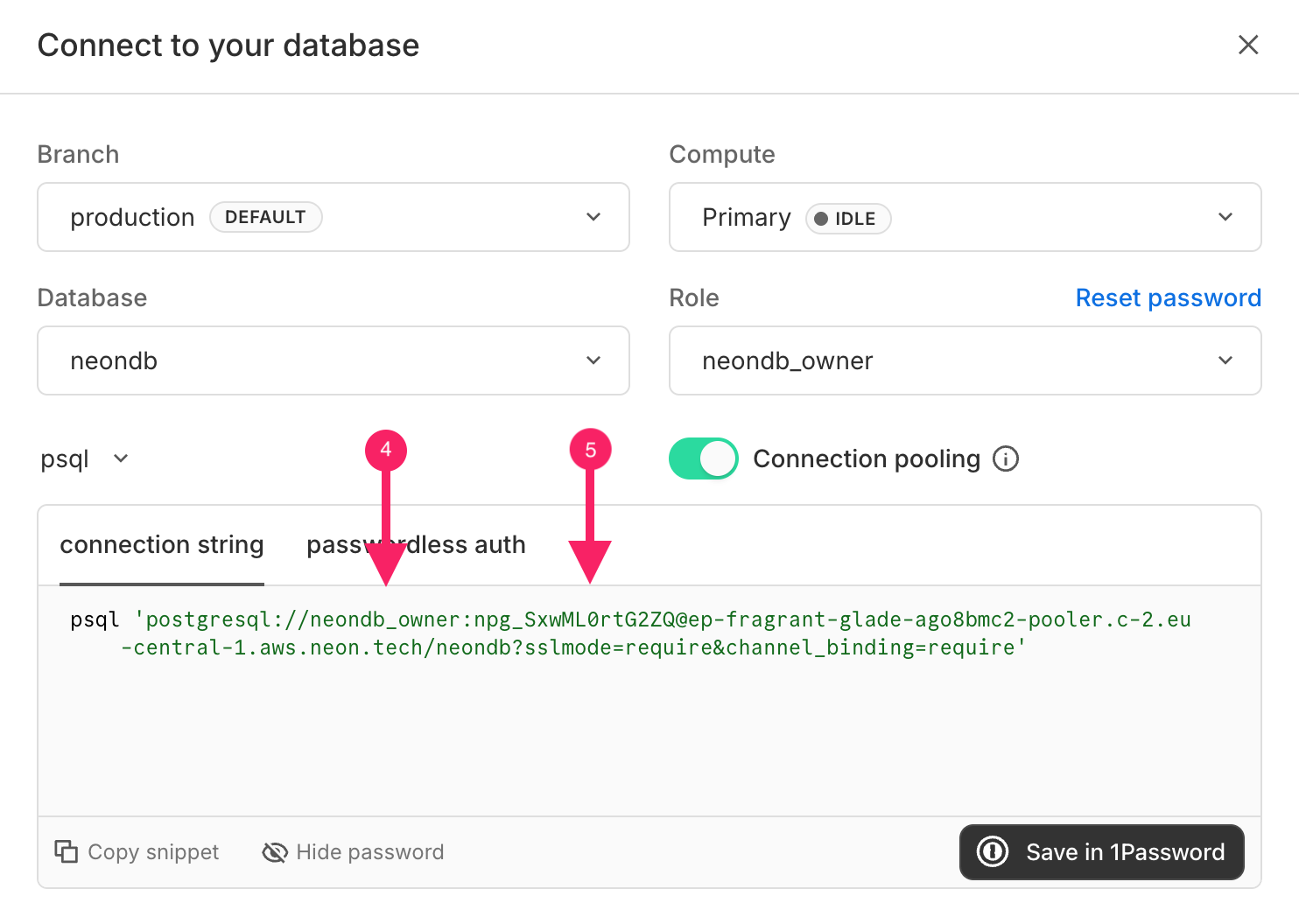
Step 2: Get your Connection String
Open your newly created Neon project.
In the Project Dashboard, click “Connect to your database.”
In the pop-up, click “Show password” to reveal your credentials.
In the connection string, you can read the user, in this example:
neondb_owner.At this part of the connection string, you can read the password - it appears right after the colon (:) following the username.
Copy your PostgreSQL connection string, you’ll need it in PocketQuery.
Step 3: Convert your PostgreSQL string to a JDBC URL
If you have this PostgreSQL connection string:
postgresql://neondb_owner:npg_SxwML0rtG2ZQ@ep-autumn-rain-agjrl0uv-pooler.c-2.eu-central-1.aws.neon.tech/neondb?sslmode=require&channel_binding=requireyou can convert it into a JDBC URL for PocketQuery in three simple steps:
1. Replace the prefix
Change
postgresql:to
jdbc:postgresql://2. Remove the credentials
Delete the username and password part (neondb_owner:npg_aPFTpcwxC09h@).
You’ll enter these separately in PocketQuery as User and Password fields.
3. Keep rest as it is
jdbc:postgresql://ep-autumn-rain-agjrl0uv-pooler.c-2.eu-central-1.aws.neon.tech/neondb?sslmode=require&channel_binding=requireFinal JDBC URL ✅
Step 4: Add your Neon database to PocketQuery
Datasource
Field | Value |
|---|---|
Name | neonDB |
Type |
|
JDBC URL | jdbc:postgresql://ep-autumn-rain-agjrl0uv-pooler.c-2.eu-central-1.aws.neon.tech/neondb?sslmode=require&channel_binding=require' |
User | neondb_owner |
Password | npg_aPFTpcwxC09h |
Step 5: Use Neon’s built-in AI SQL Assistant to enhance your workflow:
Generate realistic test data – Quickly populate your tables with sample records for dashboards or prototypes.
Fix or improve SQL queries – The AI can automatically detect syntax issues or suggest optimized query versions.
Experiment safely – Because Neon supports branches, you can test queries or schema changes without affecting your main database.
Once your changes are ready, refresh your PocketQuery view in Confluence to see the updated live data instantly.
Step 6: Create a Query in PocketQuery
In Confluence, open PocketQuery → Administration → Queries
Click Create new Query
Choose your Neon datasource from the dropdown and fill out Name and SQL Statement:
Field | Value |
|---|---|
Name |
|
SQL Statement |
CODE
|
Click Test Query – you should see tabular results showing total sales per product category.
Click Save Query to store it for later use in Confluence pages.
