Query Parameters
PocketQuery allows you to add parameters to your Query Statement. This can be done via the :parameter-syntax. Users can later define values for parameters in the PocketQuery Macro.
JDBC / SQL
Here is an example of a SQL statement with a Query Parameter:
SELECT author_id, name
FROM author
WHERE author_id > :min_author_idHere we have a single parameter called min_author_id. Notice how we expect it to be of type Integer as we are using the > operator on it. For this reason, you will need to set the type of this parameter to Integer under the Parameters tab in your Query:
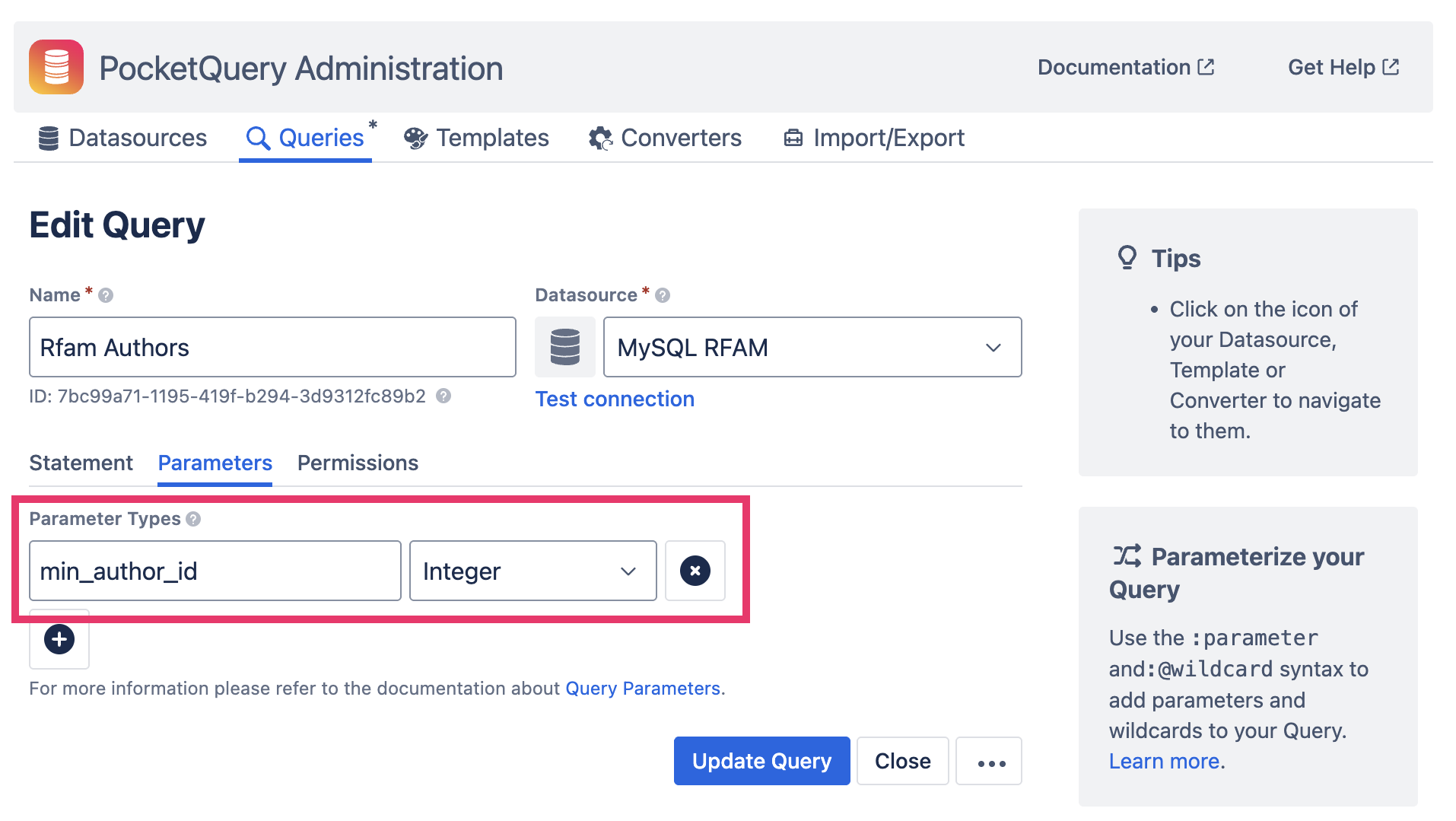
If you want to see an example of how this works, please refer to this part of our Getting Started Guide.
REST
An example REST path with a Query Parameter could look like this:
/countries/:region?limit=:max_resultsHere we have two parameters:
regionmax_results
In contrast to JDBC/SQL Queries, these values do not need a type. They will always be URL-encoded and replaced.
XML responses
PocketQuery can also understand XML responses coming from REST Datasources. If PocketQuery receives XML it will try to automatically convert it into JSON before processing it further. Enable the debug mode of your macro to see details about the transformation.
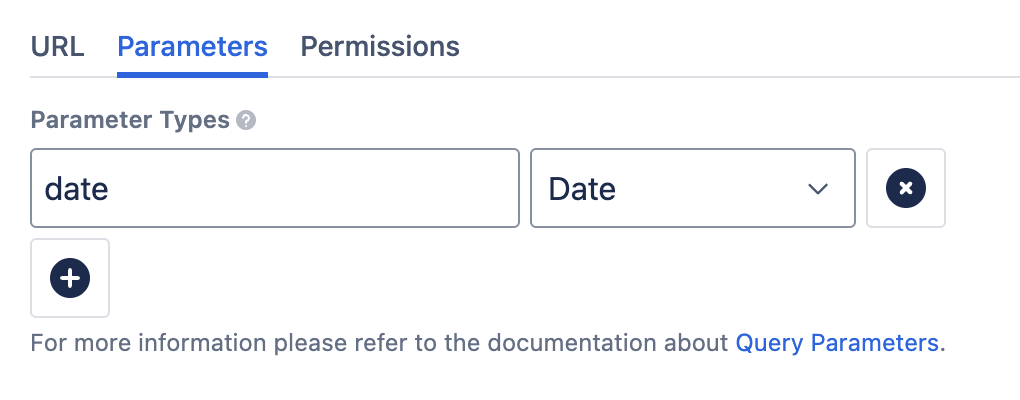
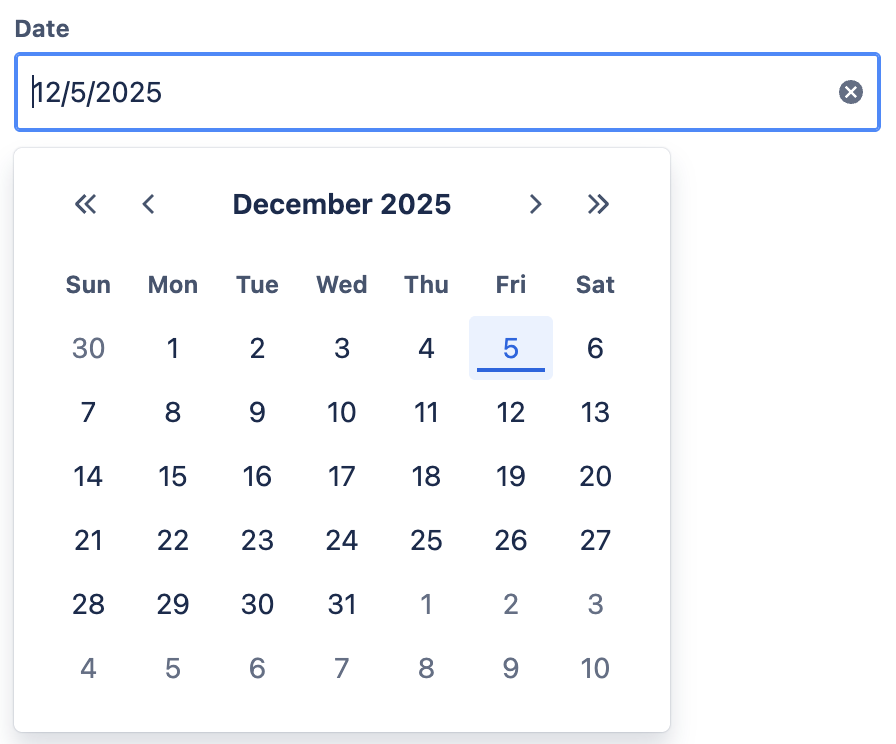
Date Type Parameter
When a parameter is set to Date, a date picker will appear in both the Macro Editor and in editable parameters for users. This makes it easier to select and input dates when running a Query:
 |  |
