HubSpot Contacts [REST Custom]
PocketQuery allows you to connect directly to HubSpot’s REST API and query your CRM data with a wide range of objects, such as Contacts, Companies, Deals, and Discounts. You can use PocketQuery to fetch, filter, and explore this data just like any other data source.
In the examples below, we’ll demonstrate how to connect to the Contacts API. The same approach works for any other HubSpot object - simply adjust the endpoint URL accordingly. For detailed information on available endpoints and object types, refer to the HubSpot CRM API documentation - all available objects are listed in the sidebar.
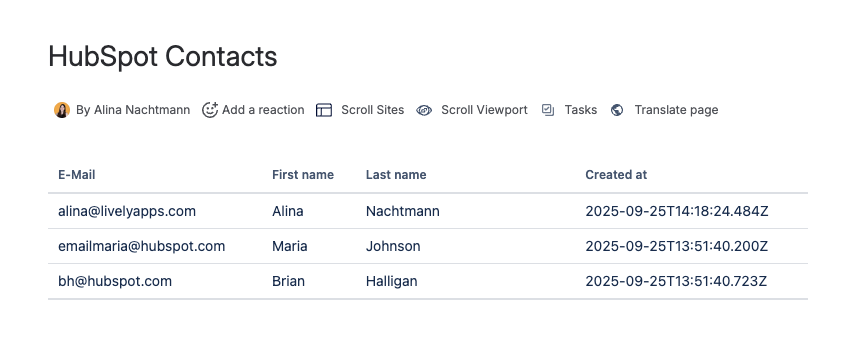
Preview
Step 1: Create a private app in HubSpot
Sign into HubSpot as a Super admin.
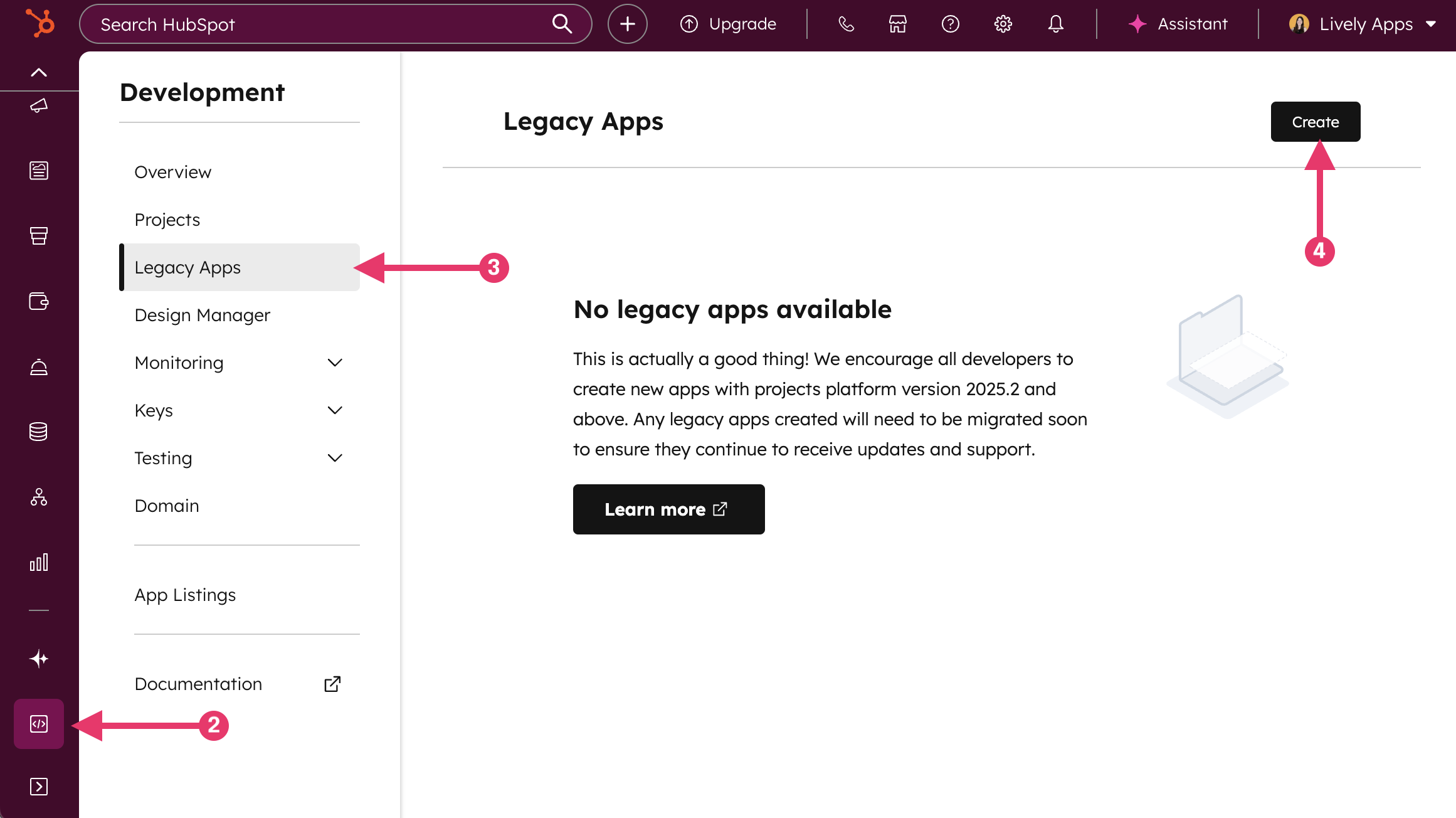
In your HubSpot account, navigate to Development.
In the left sidebar menu, navigate to Legacy apps.
In the top right, click Create:
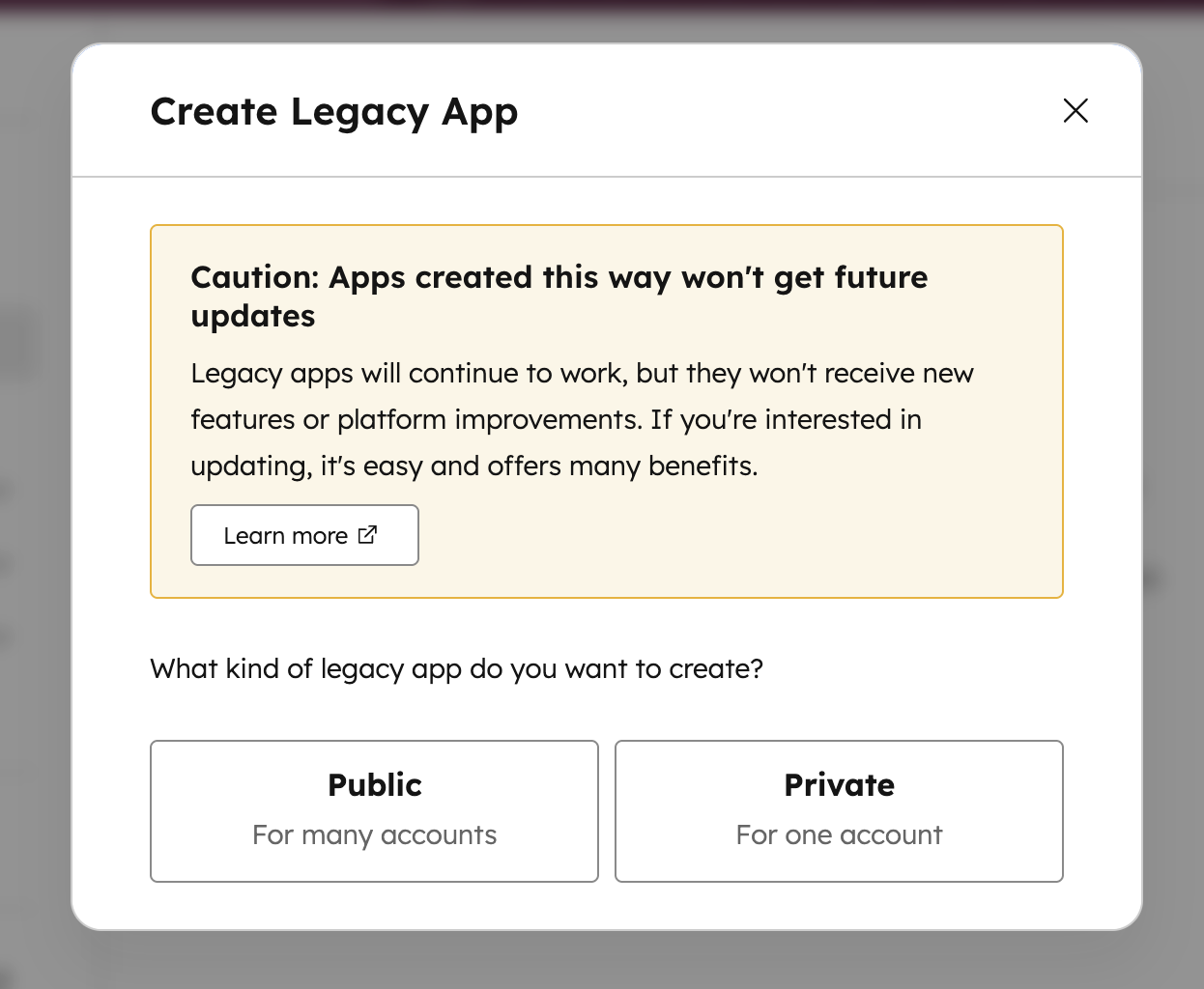
In the dialog box, select Private:
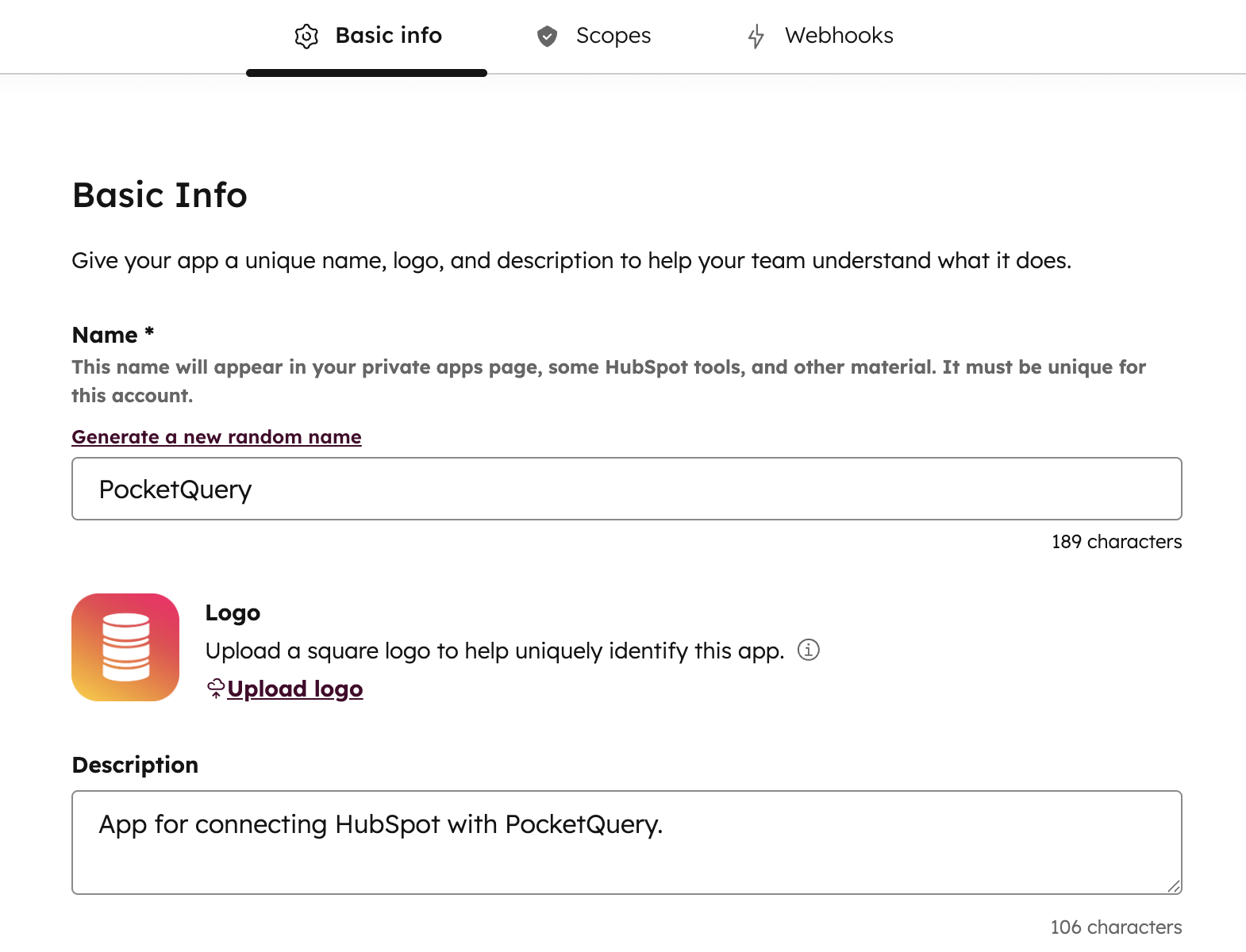
Give the app a name, logo and short description (optional):
Step 2: Choose scopes/permissions
Click the Scopes tab.
At the top of the page, click Add new scope:
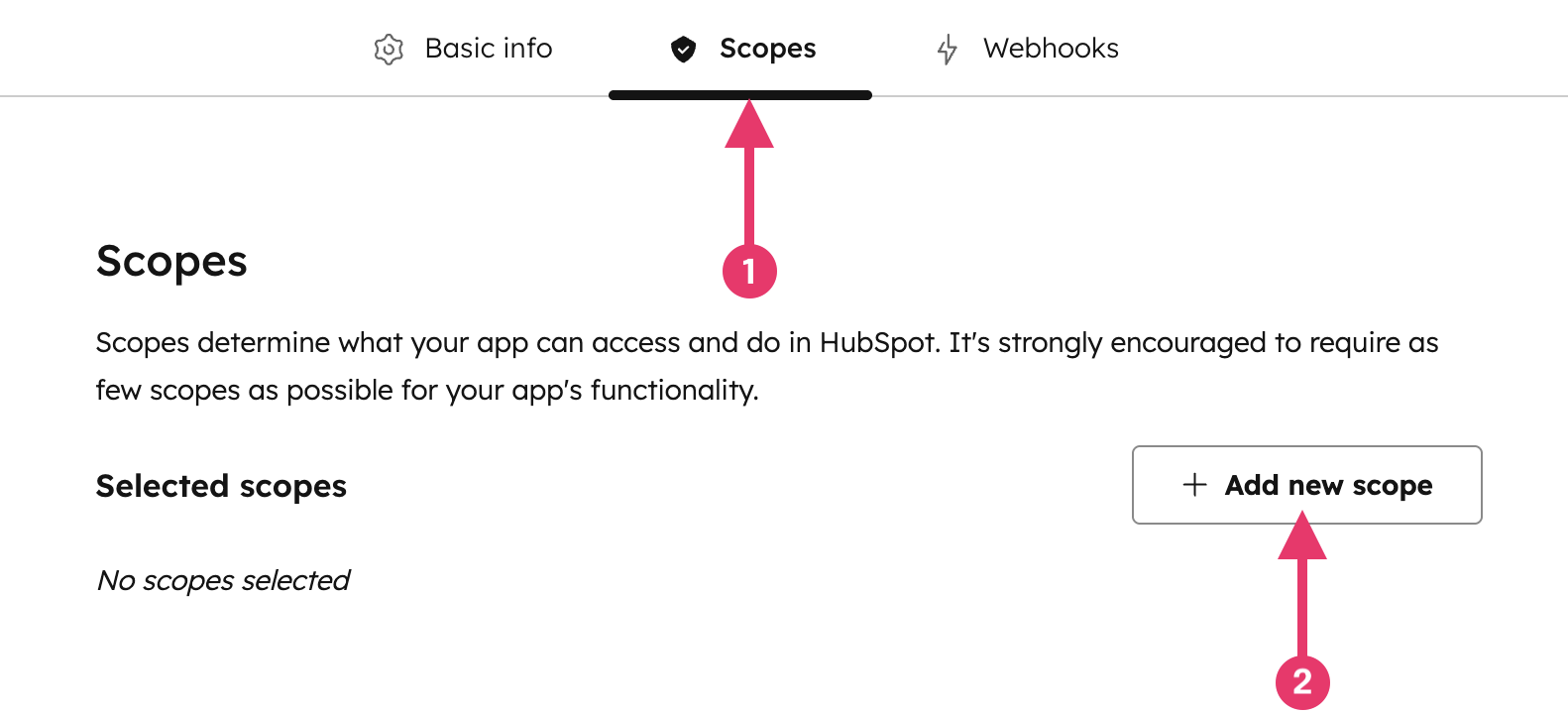
In the right panel, select the checkbox for each scope you want your private app to be able to access. In our example, wanting to read contacts, add:
crm.objects.contacts.read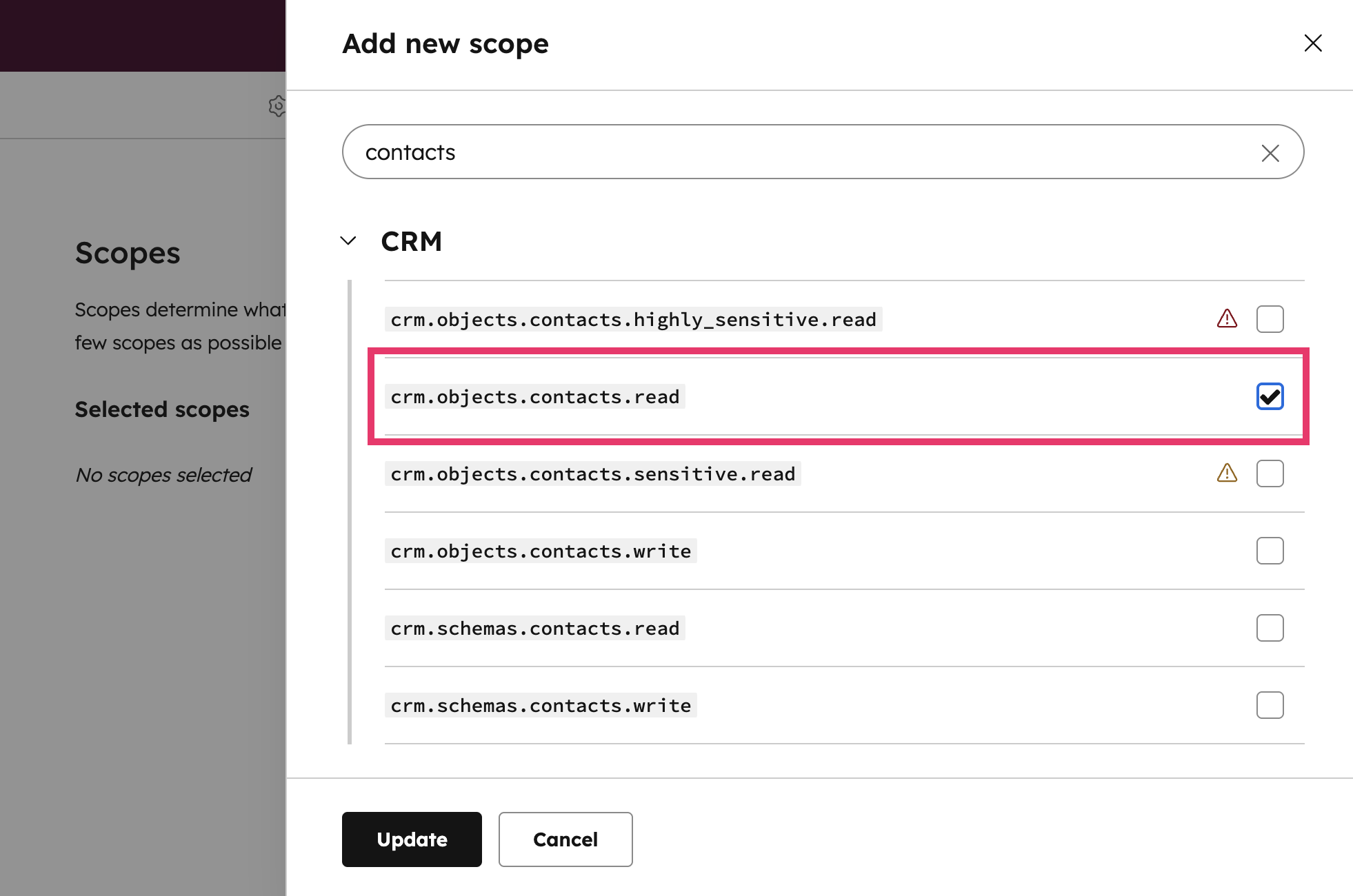
If you want Companies / Deals / etc, add:
crm.objects.companies.read,crm.objects.deals.read, ...
After you’ve chosen your scopes, click Create app:
Step 3: Get your access token
After you finish creating it, HubSpot will redirect you to the app overview (Development → Legacy apps → name of your app).
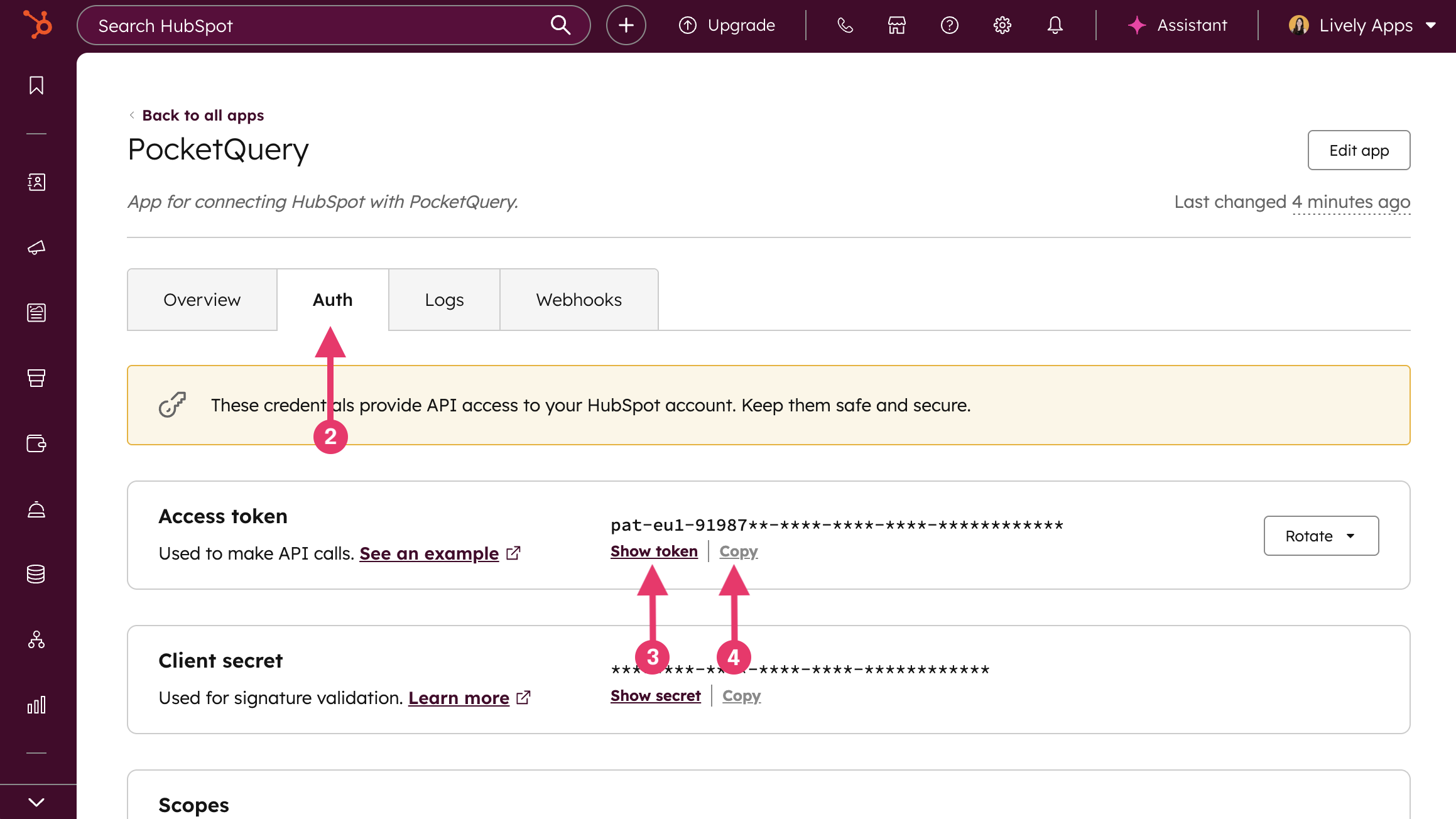
Go to the Auth tab.
Inside the Access Token box, click Show token.
…and then Copy:
Step 4: Create a Datasource in PocketQuery
Open PocketQuery Administration → Datasources, and create a new REST datasource:
Field | Value |
|---|---|
Name |
|
Type |
|
Base URL |
|
Test path |
|
Request Headers (left field) |
|
Request Headers (right field) |
(replace “<your-access-token>” with the access token you copied in Step 3) |
You can now test your connection by clicking the Test connection link at the bottom. If everything works as expected, click Create Datasource.
Step 5: Create a Converter in PocketQuery
Go to PocketQuery Administration → Converter, and create a new Converter. This will display your result data in a neat table:
function convert(json) {
const data = JSON.parse(json);
return data.results.map(contact => {
return {
'E-Mail': contact.properties.email,
'First name': contact.properties.firstname,
'Last name': contact.properties.lastname,
'Created at': contact.properties.createdate,
};
});
}Step 6: Create a Query in PocketQuery
Go to PocketQuery Administration → Queries, and create a new Query that fetches your contacts.
Field | Value |
|---|---|
Name |
|
Datasource |
|
Converter | Name of Converter created in Step 5 |
REST URL |
|
That’s it! After clicking Save Query, you can test your query in the Query Preview and use it on any Confluence Page with the PocketQuery Macro:

